2460 Software Safety and Security
#moc
- Risk Analysis
- X.509 Email Address Vulnerability
- Formal Specification
- Model Checking
- Software Model Checking
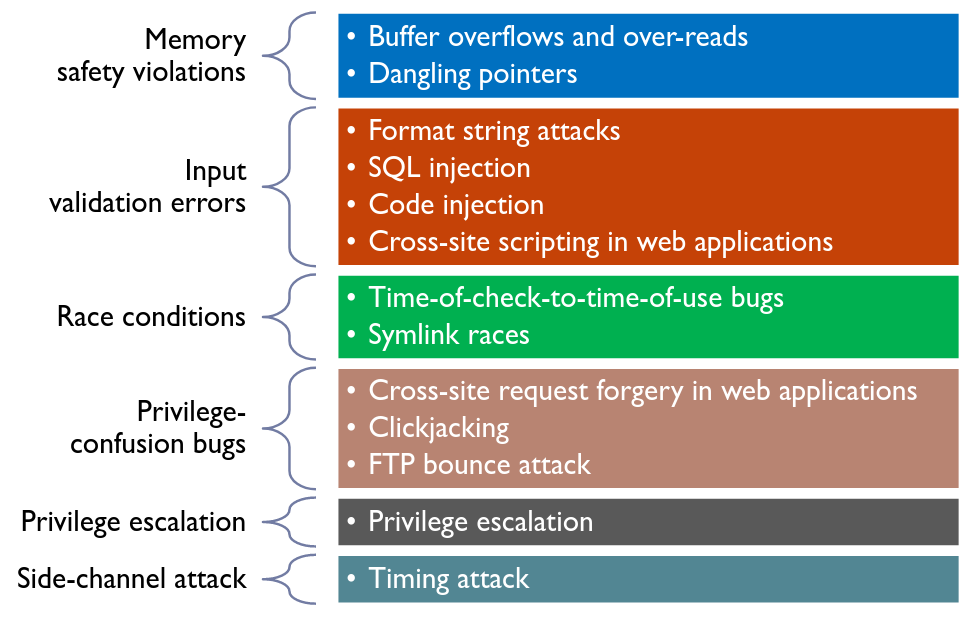
- Memory Safety
- Other Vulnerabilities
- Authentication
Safety: condition of being protected from harm Security: degree of protection from harm
# Verification vs Validation
Verification: does the software do things right?
- can be automated by tools to verify specific properties Validation: does the software do the right thing?
- requires human judgement to think about which are the correct requirements/operations
# Verification
Dynamic analysis: performs at run time analysing the real state of the system
Static analysis: performs at compile time to analyse the simplified state of the system

# Trust
Trust is what we expect the entity to do and not to do.
# Trusted Computing Base
A set of system components that need to be trusted to ensure security.
# Threat Model
A threat model needs to describe:
- What is trusted
- Resources and knowledge/actions the untrusted entities can do
- Security properties we aim to achieve
An example: phishing email – a malicious email with malware as the attachment
- What is trusted: hardware and OS
- What is not trusted: the email attachment.
- Adversarial capabilities: running malicious code in your computer.
- Security properties: protect the computer system such that the malware cannot steal the sensitive data, or tamper with other processes.
# Security properties
- Authenticity
- Confidentiality: prevent disclosure of information
- Integrity: prevent modification
- Availability: prevent withholding of information, resources should always be available (DDOS attacks)
- Accountability: actions of an entity can be traced and identified
- Non-repudiation: unforgeable evidence that specific actions occur
# Security Strategies:
- Prevention
- Detection
- Reaction
# Vulnerabilities
- Vulnerability: the weakness of a program that reduces its information assurance
- Exploit: the technique the attacker takes to compromise the target system
- Payload: the code the attacker wants the system to run.
# Side channel attack
An attack which is based on extra information that can be gathered because of the fundamental way a computer protocol or algorithm is implemented, rather than flaws in the design of the protocol or algorithm itself.
- Timing attack: based on measuring how much time various computations (such as, say, comparing an attacker’s given password with the victim’s unknown one) take to perform.
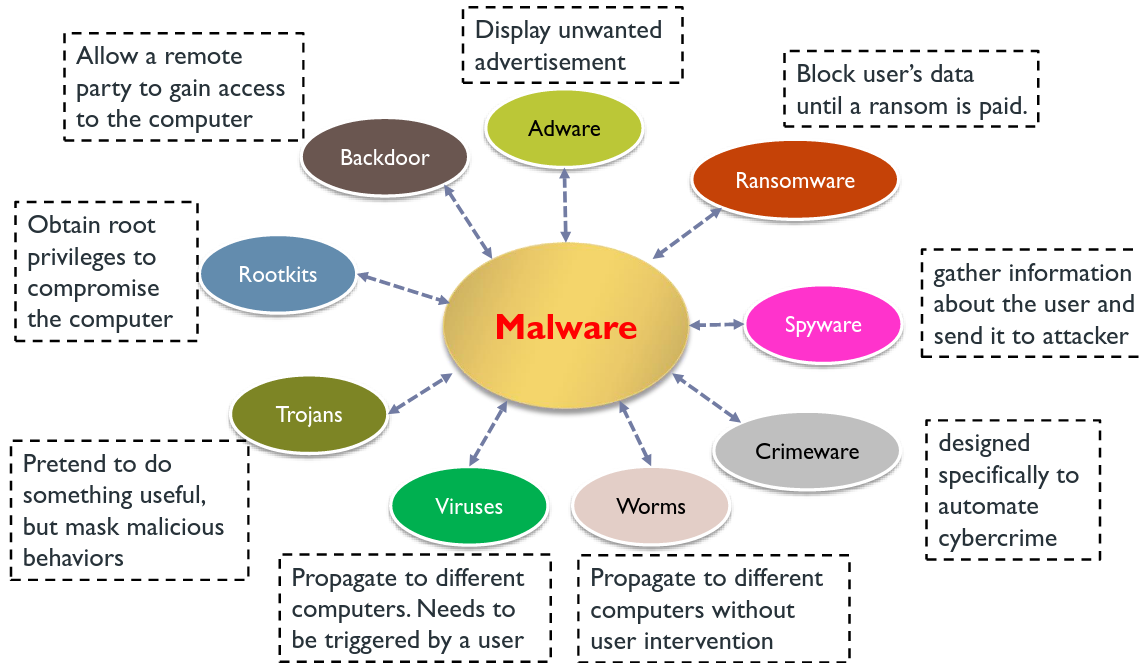
# Types of malware:
# Cyber Kill Chain
7 steps developed by Lockheed Martin which identifies what adversaries must complete in order to achieve their objectives starting from reconnaissance to data exfiltration.
- Reconnaissance: harvesting email addresses etc.
- Weaponization: coupling exploit with backdoor into deliverable payload
- Delivery: delivering payload via email, USB etc.
- Exploitation: exploit a vulnerability to execute code on victim system
- Installation: install malware on the asset
- Command and Control (C2): command channel for remote manipulation
- Actions on objectives: accomplish goal
# Case Study (SingHealth)
- The crown jewels of the SingHealth network is the electronic patient medical records stored in the SCM database, an medical record software solution.
- Users access the SCM through Citrix servers
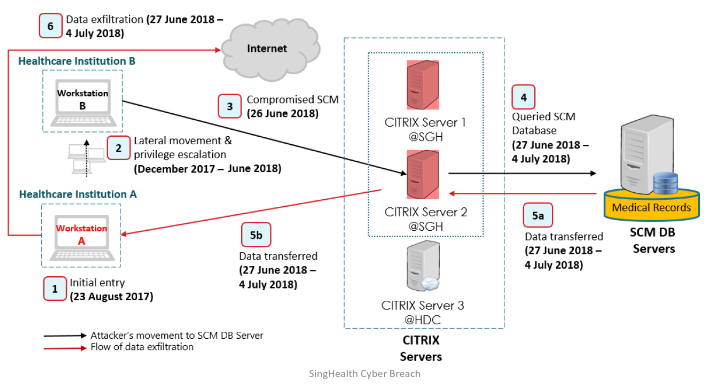
# Key events
- Attackers gain access into network by infecting front end workstations. They then laid dormant for 4 months before starting lateral movement, compromising many endpoints, servers and administrator accounts
- Attacker remotely connected to Citrix servers and began ex-filtrating patient records undetected.
- Used a customised Remote Access Trojan to enable remote shell access to download and upload malicious files. This could not be detected by standard anti-malware solutions
- Publicly available hacking tool allowed for persistent presence of the account even if the password has been changed
- Suspicious queries were noticed but were reported to IHiS senior management only 1 month later.
- No controls to detect and block bulk queries. Database activity monitoring was not implemented.
# Why
- IHiS staff did not have adequate levels of cyber security awareness, training and resources.
- Key staff in IHiS failed to take appropriate effective and timely action to prevent the data ex-filtration
- There were a number of vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the network which could have been remedied before the attack.
- Remote access was not regulated with firewalls. Unnecessary open connections between servers and database were allowed.
- Internet connectivity was not needed but increased attack surface.
- 2FA could be bypassed
- Vulnerabilities in Outlook mail software were not patched.
- Inactive accounts were not removed immediately
- Attacker was a skilled and sophisticated actor
- Employed advance tools, techniques and procedures
- Suite of advanced and customised malware
- Persistent, having established multiple footholds and backdoors
- Extensive C2 network
- Although cyber defences will never be impregnable, there were opportunities to reduce the success of the attacker.
# Recommendations
- Enhance security structure and readiness. Cyber security must be viewed as a risk management issue rather than just a technical one.
- Cyber stack must be reviewed to assess if its adequate. Gaps in cyber stack must be found by comparing with existing security technologies.
- Staff awareness must be improved through increasing knowledge.
- Enhance security checks especially on C2 systems. Vulnerability assessments, certification of vendor products and pen-testing must be conducted regularly.
- Privileged administrator accounts must be subject to tighter control and monitoring. 2FA, passphrases, password policies must be implemented and enforced.
- Incident response process must be improved with predefined modes of communication.
- Partnership with industry leaders in cyber security