Other Vulnerabilities
# Other Vulnerabilities
# Format Strings
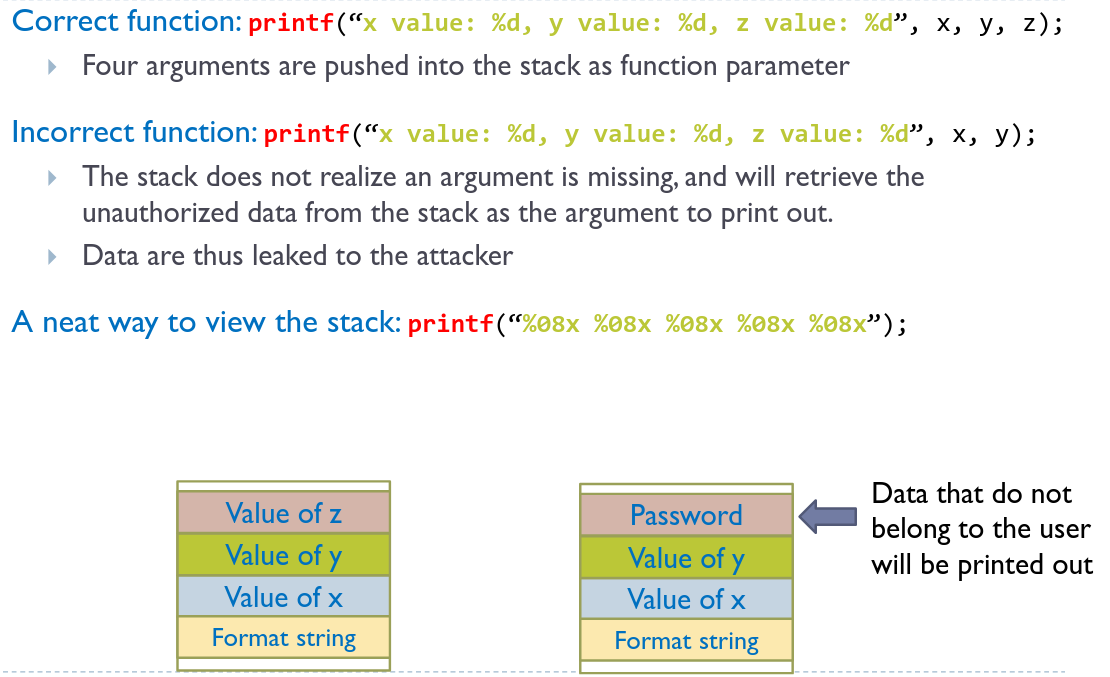
The root cause behind format string vulnerabilities is that the number of arguments do not match the number of format sequences.
# Leaking the stack
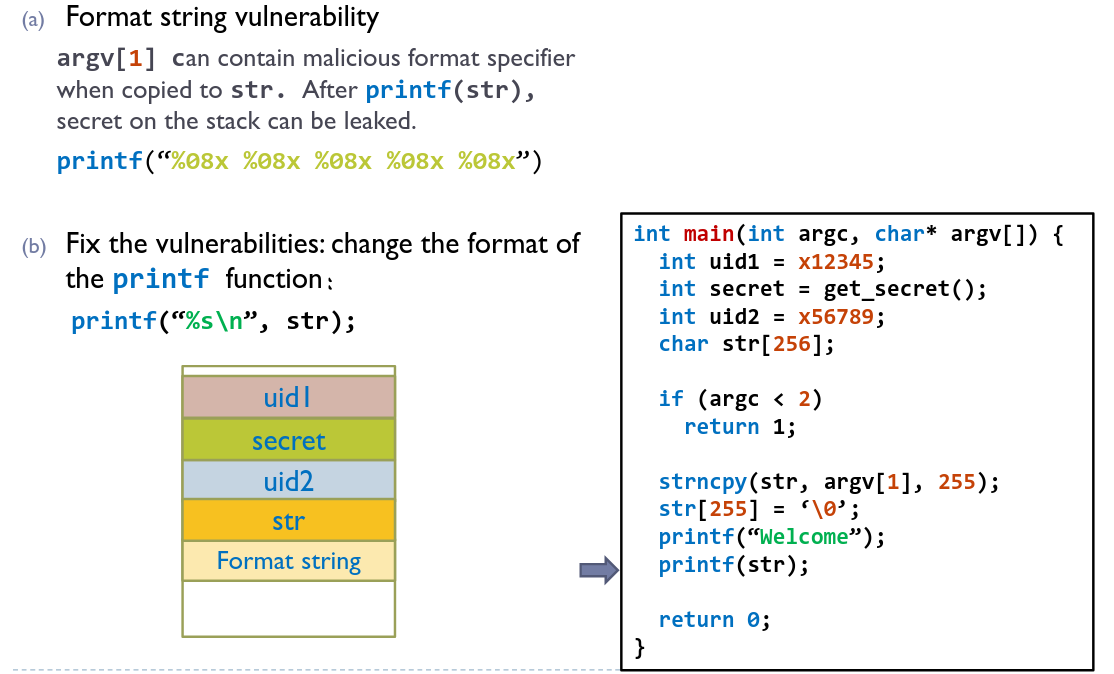
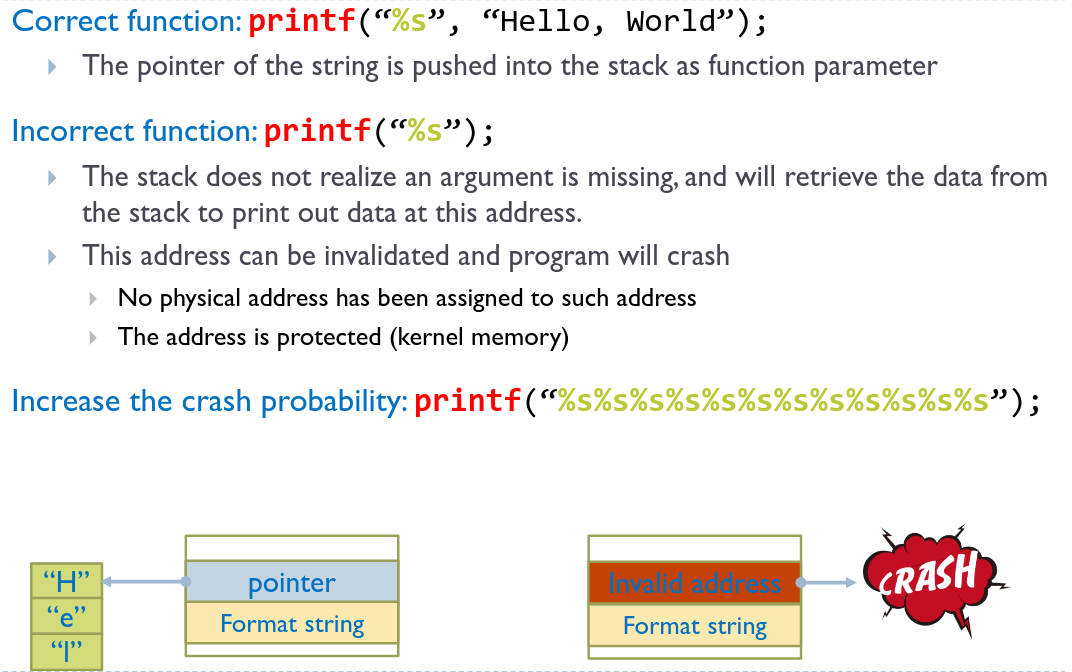
# Crashing the program
# Modifying memory
The format string %n does not print anything, instead it stores the number of characters printed so far and can be used to store this value in an address.

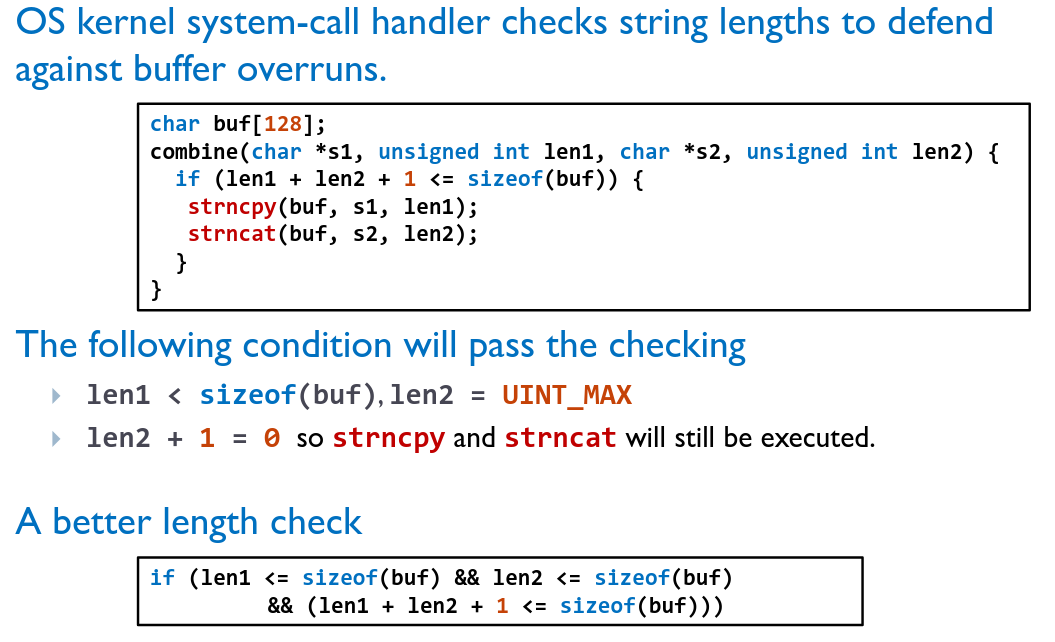
# Integer Overflows
# Scripting Vulnerabilities
Construct commands from predefined code fragments and user input at run time.
# Cross Site Scripting (XSS) attacks
Exploit websites which receive user input to inject executable malicious code into the website.
# Stored (Persistent)
Stored cross-site scripting (also known as second-order or persistent XSS) arises when an application receives data from an untrusted source and includes that data within its later HTTP responses in an unsafe way.
Suppose a website allows users to submit comments on blog posts, which are displayed to other users. Users submit comments using an HTTP request like the following:
| |
After this comment has been submitted, any user who visits the blog post will receive the following within the application’s response: This post was extremely helpful.
Within the attacker’s request, this comment would be URL-encoded as: `comment=%3Cscript%3E%2F*%2BBad%2Bstuff%2Bhere…%2B*%2F%3C%2Fscript%3E
Any user who visits the blog post will now receive the following within the application’s response:
<p><script>Bad stuff here</script></p>
# Reflected
Reflected cross-site scripting (or XSS) arises when an application receives data in an HTTP request and includes that data within the immediate response in an unsafe way.
Suppose a website has a search function which receives the user-supplied search term in a URL parameter: https://insecure-website.com/search?term=gift
The application echoes the supplied search term in the response to this URL:
<p>You searched for: gift</p>
Assuming the application doesn’t perform any other processing of the data, an attacker can construct an attack like this:
https://insecure-website.com/search?term=<script>/Bad+stuff+here</script>
This URL results in the following response:
<p>You searched for: <script>Bad stuff here</script></p>
# Examples
| |
- Buffer overflow
- title + rest of the string can be > 512 bytes
- Format string
bodycan contain malicious string like%s%s%stofprintf, potentially leaking the stack
- Scripting
- title can contain malicious command:
title = empty” foo@bar.com; rm –rf /; buf = mail –s “Subject: empty” foo@bar.com; rm –rf /; ” fake-addr@ntu.edu.sg - All the files on the server will be removed.
- title can contain malicious command: